Understanding GERD: Causes, Symptoms, and How to Manage It Effectively
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) is a chronic digestive disorder where stomach acid or bile flows back into the esophagus, irritating its lining. This condition can lead to discomfort and complications if left untreated. In this article, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies for GERD.
Causes of GERD
GERD occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a ring of muscle that acts as a valve between the esophagus and stomach, weakens or relaxes abnormally. Common causes include:
- Obesity: Excess weight can increase pressure on the abdomen, pushing stomach contents into the esophagus.
- Hiatal Hernia: A condition where the stomach bulges into the chest through the diaphragm.
- Dietary Habits: Consuming spicy, fatty, or acidic foods, as well as caffeine and alcohol.
- Smoking: Weakens the LES and increases acid production.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and pressure from the growing uterus can trigger GERD.
Symptoms of GERD
The most common symptoms of GERD include:
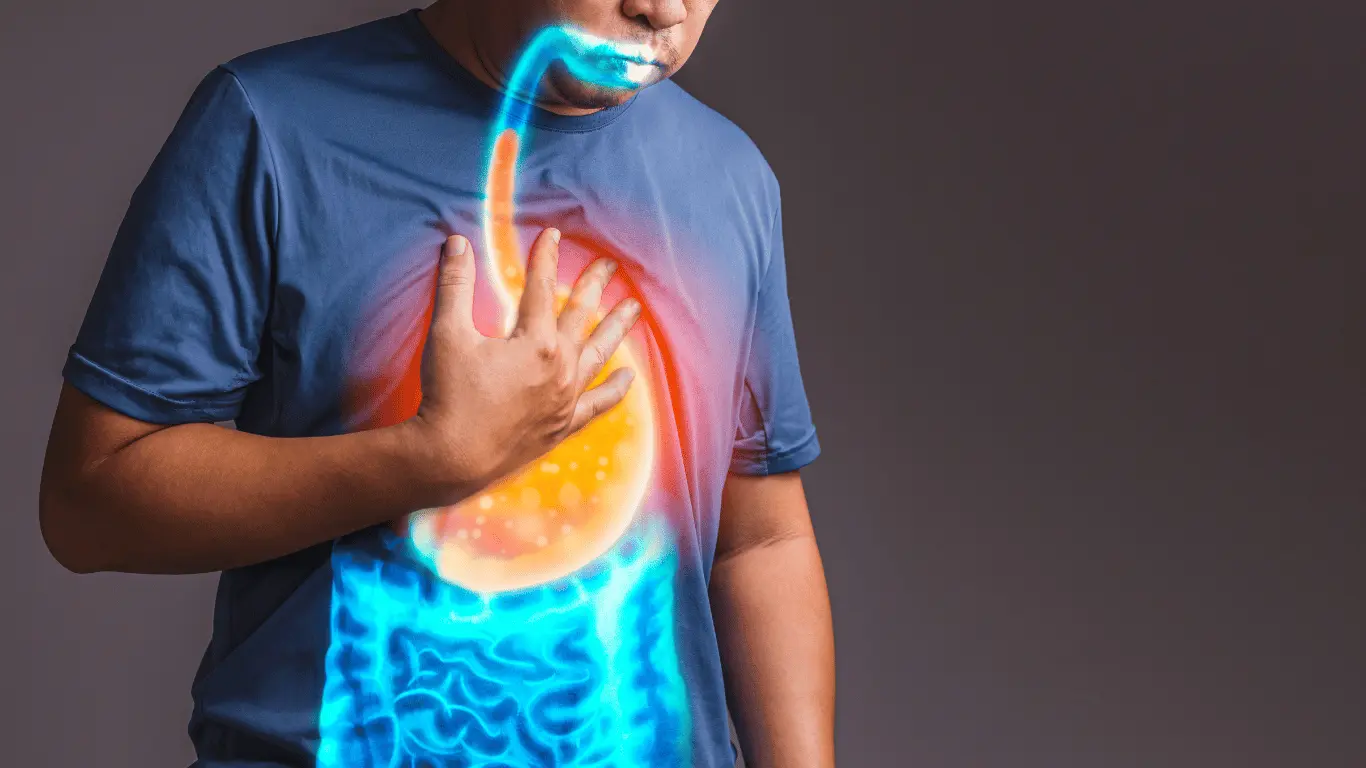
- Heartburn: A burning sensation in the chest, often after eating.
- Regurgitation: Sour or bitter-tasting acid backing up into the throat or mouth.
- Difficulty Swallowing: A feeling of food being stuck in the throat.
- Chest Pain: Often mistaken for heart-related issues.
- Chronic Cough or Sore Throat: Caused by acid irritating the throat.
How to Manage GERD Effectively
Managing GERD involves lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes surgical interventions. Here are some effective strategies:
- Dietary Adjustments: Avoid trigger foods, eat smaller meals, and avoid lying down immediately after eating.
- Weight Management: Losing excess weight can reduce pressure on the abdomen.
- Elevate the Head of Your Bed: This helps prevent acid from flowing back into the esophagus.
- Medications: Antacids, H2 blockers, and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) can help reduce acid production.
- Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: Both can weaken the LES and worsen symptoms.
